Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway
This article may be written from a fan's point of view, rather than a neutral point of view. (December 2018) |
| Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway | |
|---|---|
 | |
 1926 map of S&DJR | |
| Overview | |
| Status | Mostly disused (part reopened) |
| Owner |
|
| Locale | Somerset Dorset |
| Termini | |
| Stations | 48 |
| Service | |
| Type | Heavy rail |
| Services | Bath to Bournemouth, Bridgwater to Bournemouth, Burnham to Bournemouth |
| Depot(s) | Highbridge Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Works; Bournemouth |
| History | |
| Opened | 1854 (Somerset Central Rly.), 1860 (Dorset Central Rly.), 1874 (extension) |
| 1862 | SCR and DCR amalgamate to form Somerset & Dorset Railway |
| 1876 | S&DR becomes S&DJR under joint ownership by Midland Rly. and London & South Western Rly. |
| Closed | 1951-1966 |
| Reopened | 1996 (1 mile of line relaid by Somerset & Dorset Railway Heritage Trust to date) |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 105 miles 45 chains (169.9 km) (1925)[1] |
| Track length | 180 miles 62 chains (290.9 km) (1925)[1] |
| Number of tracks | Majority single track. 45 miles 3 chains (72.5 km) double track.[1] |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Old gauge | 7 ft 1⁄4 in (2,140 mm) Brunel gauge |
| Highest elevation | 811 ft (247 m) between Binegar and Masbury[1] |
| Maximum incline | 1 in 50 between Bath and Midford, Radstock and summit of Mendip Hills, and summit and Evercreech[1] |
Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This diagram shows the maximum extent of the line. All distances and timings are cumulative from Bath Green Park railway station. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR, also known as the S&D, S&DR or SDJR), was an English railway line jointly owned by the Midland Railway (MR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) that grew to connect Bath (in north-east Somerset) and Bournemouth (then in Hampshire; now in south-east Dorset), with a branch in Somerset from Evercreech Junction to Burnham-on-Sea and Bridgwater. Strictly speaking, its main line only ran from Bath Junction to Broadstone, as the Bath to Bath Junction section was wholly owned by the MR and the Broadstone to Bournemouth section was owned by the LSWR.[2]
Brought under joint ownership in 1876, the S&DJR was used for freight and local passenger traffic over the Mendip Hills, and for weekend holiday traffic to Bournemouth. Criticised as the "Slow and Dirty" or the "Slow and Doubtful", it closed in 1966 as part of the Beeching axe despite protests from the local community.
Overview
[edit]The initial Somerset and Dorset Railway (S&DR) was created on 1 September 1862 by an amalgamation of the Somerset Central Railway (SCR; opened in 1854) and the Dorset Central Railway (DCR; opened in 1860). The SCR line ran from Highbridge to Templecombe and the DCR line from Blandford to Wimborne, and by 1863 when a line connecting them was opened, the Somerset and Dorset Railway ran from Burnham-on-Sea to Wimborne, where S&DR trains could use a line owned by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) to reach Poole Junction (now Hamworthy) on the Dorset south coast.
This cross-country link between the Bristol Channel and the English Channel failed to attract the substantial traffic expected and so the S&DR, falling into dire financial straits, made a desperate bid to increase their prospects by building an extension from Evercreech Junction to Bath in 1874, to link with the Midland Railway. This provided a through route between the south coast and Midlands and north and produced a substantial increase in traffic, but came too late to save the company. The S&DR went into receivership and in 1875 it became jointly owned by the Midland Railway and the LSWR,[2] and was renamed the Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR). After the 1 January 1923 Grouping, joint ownership of the S&DJR passed to the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and the Southern Railway.[3][4]
Its attractions were its quirky individuality, its varied scenery (captured particularly by the photographs and pioneering cine films taken by Ivo Peters), and the way it seemed to struggle against overwhelming odds. Its main line climbed to 811 feet (247 m) above sea level at Masbury, and it contained several single line sections, but on summer Saturdays it managed to handle a considerable volume of holiday trains, when it seemed every possible locomotive was drafted into service to handle heavy trains requiring double-heading and banking over the steep gradients.
The S&DJR started before the railway network in England had settled down, and both local and strategic aspirations structured the line's earliest days. Work has now started to restore some remnants of the line to working condition, notably at Midsomer Norton in Somerset and Shillingstone in Dorset.
The S&D in the early 1960s
[edit]The fame of the Somerset & Dorset line reached its peak in the first years of the 1960s, just before final closure as part of the nationwide reduction of railway services, usually called the Beeching Axe.
The main line was still active, carrying local passenger trains and a daily long-distance train, the Pines Express, from Manchester to Bournemouth West, reversing at Bath Green Park. Local freight on the route survived in adequate volumes, although the Somerset coalfield was becoming ever more uneconomic to work and so coal traffic had dwindled.[5]
On summer Saturdays, the line continued to carry a very heavy traffic of long-distance trains, from northern towns to Bournemouth and back. The traditional nature of the operation of the route was reflected in the fact that most of the originating towns were on the former Midland Railway system, almost as if the railway grouping of 1923 had never taken place. These trains brought unusual traffic combinations to the route, and the home locomotive fleet was augmented by strangers such as LMS Jubilee Class 4-6-0s from the north, though these did not work over the S&D proper, and West Country Pacifics from the south. For the summer seasons of 1960, 1961 and 1962 a small number of BR Standard Class 9F 2-10-0s, which were designed as heavy freight locomotives, were transferred to Bath locomotive depot, in an attempt to reduce the preponderance of double-heading required on the majority of trains between Bath and Evercreech Junction on account of the steep gradients encountered on either side of Masbury summit. For the same reason, during the summer months the native S&D class 7F 2-8-0s were also pressed into service to assist, or to handle lighter trains on their own.
The route remained almost entirely steam-worked until closure, though some diesel multiple units ran over the line on a couple of excursions only in the final years.[6] After closure, diesels worked demolition trains, and some diesel workings operated to Blandford Forum after the line had closed.[7]
Freight in the 1960s was largely in the hands of Fowler 4Fs, Stanier 8Fs, Standard Class 5 4-6-0s, and the S&DJR 7F 2-8-0s, assisted by Fowler 3F "Jinty" 0-6-0Ts and Great Western Railway Pannier Tanks; freight trains were assisted in rear by these locomotives over the Combe Down summit and over Masbury.
The Highbridge branch trains were latterly worked by GWR 2251 Class 0-6-0s, and LMS Ivatt Class 2 2-6-0.s
Geography
[edit]
The S&D main line ran south from Bath Queen Square (later renamed Green Park) to Radstock, at one time the centre of the Somerset coalfield, and then over Masbury Summit, at 811 feet (274 m) above sea level, crossing the Mendip Hills, via Shepton Mallet and entering the catchment area of the River Stour to Wincanton and Blandford, joining the LSWR South West Main Line at Poole, the S&D trains continuing to the LSWR station at Bournemouth West.[8]
The branch line from Highbridge to Evercreech Junction had been the original main line, when attracting steamer traffic across the Bristol Channel had been an objective. It traversed a sparsely populated area, and when the marine connection ceased, only Glastonbury and Street in the centre of the route contributed any worthwhile income. There had been other, shorter branches, but these too generated very little traffic and they had all closed by the early 1950s.[9]
Serving only a string of medium-sized market towns between its extremities, the S&D generated a modest internal traffic, and had daunting operational costs, due to the difficulty of its main line. Its strategic significance was as part of a through route between the Midlands and the South Coast, by connecting with the Midland Railway at Bath. The Midland Railway linked Bath to Bristol and via Gloucester to Birmingham and the north. Heavy summer holiday passenger traffic and healthy through freight business was the result, but the long and difficult main line was always very expensive to run.[10]
There was only one intermediate connection on the route, at Templecombe where the West of England line was crossed. There was an awkward layout there, requiring through trains to reverse along a spur between the S&D main line and the east-west LSWR main line.[11] The full journey time for ordinary passenger trains was typically four hours, although the limited stop holiday expresses managed it in two hours.
Much of the S&D was single track, but the main line was double track from Midford to Templecombe, and from Blandford Forum to Corfe Mullen. Crossing trains on the single line sections always added operational interest to the line, but many enthusiasts chose to focus on the quirky operation of trains calling at Templecombe and the light engine movements associated with them. Trains had to reverse from Templecombe station to Templecombe Junction (for southbound trains, and the reverse for northbound), requiring use of a pilot engine to assist with these manoeuvres. In at least one case, a northbound train and a southbound train, both requiring to call at Templecombe station, were timed to arrive at Templecombe Junction simultaneously. The operating procedure was for the northbound train to set back on to the southbound train at the junction, thence to be pulled into the station by the southbound train engine, with the northbound engine still on the back. After completion of station work, the entire equipage was pulled back to the junction by the northbound train engine, where the two trains were uncoupled to continue on their separate ways.
History
[edit]The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway came into existence on 1 November 1875.[12] It was formed when the Somerset & Dorset Railway ran into unmanageable financial difficulties and they leased the line for 999 years to the Midland Railway and the London and South Western Railway jointly.[4]
The origins of the Somerset & Dorset Railway lay with two separate companies, which built sections of line, each with their own ambitions.
Somerset Central Railway
[edit]The Somerset Central Railway started out as a local railway line designed to give Glastonbury transport access for manufactured goods, to the Bristol Channel and to the Bristol and Exeter Railway's main line. It soon saw that a longer connection southwards was useful, and made an alliance with the Dorset Central Railway, and built an easterly line to join that railway at Cole.
Origins
[edit]
The Somerset Central Railway opened on 28 August 1854 from Glastonbury to Highbridge Wharf.[12] Glastonbury was then an important manufacturing town, but its location made the transport of goods difficult. Coastal shipping was still dominant for transport and the Bristol Channel ports of Bridgwater and Highbridge were about 18 miles away. The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) had been opened, passing through both those towns, in 1841.
Highbridge was chosen as the destination because a route to Bridgwater would have been much more challenging technically, because of high ground to the east of Bridgwater itself. The Glastonbury Canal had been bought by the friendly B&ER, and by arrangement with them the canal was closed and the railway built partly on the course of the canal, reducing construction cost.
The line was opened as 7 ft 1⁄4 in (2,140 mm) broad gauge, as a feeder to the B&ER, and had stations at Glastonbury, Ashcott, Shapwick, Edington, Bason Bridge (opened in 1862) and Highbridge at the B&ER station.[13] There were goods facilities at Highbridge Wharf, to the west of the B&ER line. The line was worked operationally by the B&ER.
Initial results were encouraging, and the original objective of the railway, to give Glastonbury access to the maritime and railway transport links at Highbridge, was successfully achieved.
Development
[edit]Highbridge Wharf became a hive of activity, and at this early date coastal shipping was still an important means of transporting goods. To reach South Coast destinations the ships had a difficult and hazardous passage round Land's End, and there were hopes that the railway could become the core of a transport chain bringing manufactured goods, especially metal goods, from South Wales to the Southern Counties, and taking agricultural produce back to feed the industrial population in South Wales, using shipping across the Bristol Channel.[14]
The success of Highbridge Wharf for goods traffic encouraged ideas of expanding passenger traffic across the Bristol Channel, and on 3 May 1858 the Somerset Central Railway opened an extension from Highbridge to a new passenger pier at Burnham, expecting heavy passenger traffic. The pier was actually a slip, a broad ramp 900 feet (274 m) long, sloping down at 1 in 21 into the tidal waters; and steamers berthed alongside at the point where the adjacent part of the slip was at a suitable height.[11] Rails were laid on the slip, and single wagons were worked down to the steamers using a wire rope;[15] passengers, however, walked to a platform at Burnham station nearby. In both cases the arrangement was awkward and inconvenient, and the anticipated traffic growth never materialised, and the Burnham Pier, which had cost £20,000, was a financial failure.
At the eastern end, a branch to the important city of Wells was opened on 15 March 1859. This had originally been planned to be part of a main line extension towards Frome, where the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway could be joined, giving the yearned-for access to the South Coast towns, but by now the Somerset Central thought that joining up with the Dorset Central Railway would be a more cost-effective option. Wells therefore was a branch line only, with the station at Priory Road.[11] It too was broad gauge, and one intermediate station at Polsham was opened in 1861.
The impetus now however was the south-easterly link with the Dorset Central Railway, and parliamentary powers were sought for the extension to Cole.
The link to Cole
[edit]Cole was no destination in itself, but was the agreed point of meeting up with the Dorset Central Railway. The important town of Bruton lay nearby, but its topography made a closer approach difficult. The Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway had been opened in 1856, giving broad gauge access to the Great Western Railway (GWR) system, but the Somerset Central wanted to have through standard gauge access to the Dorset Central Railway and the South Coast. Parliamentary powers were sought and the standard gauge was specified, but pressure from the broad gauge B&ER – who feared loss of the feeder traffic from the line it had supported – led to a requirement to lay broad gauge and to make a junction with the Wilts Somerset and Weymouth where the lines would cross.
The line from Glastonbury to Cole opened on 3 February 1862 and mixed gauge track was laid, although the required connection to the Wilts Somerset & Weymouth was never opened. Glastonbury to Highbridge and Burnham was converted to mixed gauge at the same time. Intermediate stations between Glastonbury and Cole were West Pennard, Pylle and Evercreech.
Dorset Central Railway
[edit]Initial opening
[edit]The Dorset Central Railway had started with higher ambitions than the Somerset line. Its promoters had originally intended a connection to the north via Bath, but their actual railway started more modestly. It opened on 1 November 1860 from the LSWR station at Wimborne, to the important market town of Blandford. The Blandford station at this time was south of the river Stour, at the hamlet of Blandford St. Mary, until later amalgamation, when the bridge was built over the river.[12][16]
The line was worked by the LSWR. This and all of the Dorset Central Railway's lines were standard gauge. Intermediate stations were at Spetisbury, and Sturminster Marshall.
Northwards aspiration
[edit]Seeing that its northwards destiny could best be served by an alliance with the Somerset Central Railway, it obtained powers to extend to Cole and join that railway there, and it opened part of this route, from Templecombe to Cole on 3 February 1862, the same day that the Somerset company opened its section to Cole. There was one intermediate station, at Wincanton. All of this northern section was worked by the Somerset company.
Templecombe
[edit]
Templecombe was a small community and its significance was the connection to London over the Salisbury & Yeovil Railway's line. The DCR trains used the Salisbury & Yeovil Railway station on the main line. The difference in levels between the two lines and the availability of land induced the company to make the physical connection facing towards Salisbury and London, and the junction was to the east of the S&YR station. The S&YR provided a track from the point of junction back to their station, and DCR trains arriving from Cole had to reverse from the junction to the S&YR station. It is unlikely at this early date that through running (without calling at Templecombe) was contemplated, and the DCR spur probably did not connect directly into the S&YR main line.[17]
Formation of the Somerset & Dorset Railway
[edit]
The Somerset Central Railway and the northern part of the Dorset Central Railway were worked as a single unit from the beginning, and on 1 September 1862 the two railways were amalgamated[18] by Act of Parliament, under the title Somerset & Dorset Railway. At this time therefore, the system consisted of:
- the original main line and its eastward extension, running from Highbridge to Templecombe (the junction with the Salisbury & Yeovil Railway);
- the Highbridge Wharf extension and the Burnham extension at the western end;
- the separate portion from Blandford to Wimborne Junction.
Closing the gap
[edit]The new company opened the missing link from Blandford to Templecombe on 31 August 1863, and now the original dream of a link from the English Channel to the Bristol Channel materialised. The LSWR allowed through passenger trains to run over their line between Wimborne and Poole, reversing at Wimborne. The Somerset and Dorset company therefore operated trains from Burnham to Poole and on the branch to Wells. At this time Poole station was on the western side of Holes Bay, at the location that ultimately became Hamworthy Goods.
Intermediate stations between the point of junction at Templecombe and Blandford were Templecombe (S&DR station), Henstridge, Stalbridge, Sturminster Newton, Shillingstone and Blandford. The original connection from Cole to the Salisbury & Yeovil Railway (S&YR) had faced towards London, and the new line diverged half a mile or so north of the S&YR line, passing under it by a bridge. The S&D Templecombe station was provided between the new junction and the S&YR bridge. The opening of Sturminster Newton station prompted the renaming of the Sturminster Marshall station to Bailey Gate (after the adjacent turnpike gate) to avoid confusion. At Blandford, a new station was built, situated more conveniently to the town, and the earlier DCR station south of the River Stour was closed.
Templecombe complications
[edit]
Templecombe had suddenly become the most important interchange point on the system, and trains from Wimborne needed convenient access to a station. The company provided its own "Lower" station on the direct north–south line a little north of the S&YR line on the east of its own line. S&DR passengers had their own station, but the through traffic from Glastonbury and Highbridge to London was important, and would not think well of the half mile walk between the two stations. To accommodate those passengers, the S&YR operated a shuttle train service between the two stations.

This arrangement could hardly continue, but the topography of the village was challenging. The solution eventually adopted was to construct a new west-facing connection entering directly into the S&YR station. Because of the height difference it made its junction with the DCR main line some distance to the north at a new junction. The east-facing connection to the S&YR line was severed, although the spur was retained as a siding connected at the Templecombe S&DR end.
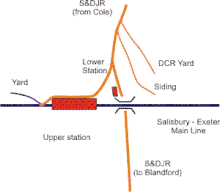
At some later date, it became obvious that the S&D station to the east of its main line was almost useless, as nearly all trains called at the main (Upper) station to make connections. The Lower station was closed and a short platform, Templecombe Lower Platform, was provided on the west side of the main line, adjacent to the main road. There were no facilities on it, and only the last train from Bournemouth and certain other very early or late trains used it.
Bournemouth reached at last
[edit]In the first half of the 19th century, Bournemouth was an insignificant hamlet, and when a railway from London to Dorchester was being planned, no importance was attached to the coastal area. Later as the town grew many of its wealthier inhabitants blocked the coming of the railway as they felt it would spoil the exclusivity of the town by allowing access to tourists from all classes. Accordingly, the railway from Southampton to Dorchester cut inland to pass through the important towns of Ringwood and Wimborne. There was a branch to the west of Holes Bay from Poole Junction (now Hamworthy) to a station called Poole, situated to the west of the bridge over the inlet. This was the "Poole" station that Somerset & Dorset trains reached over LSWR tracks, reversing at Wimborne.
This was inconvenient for the town of Poole, and the LSWR interest built a railway to reach Poole itself from Broadstone, opening on 2 December 1872, and through a daughter company from Poole to Bournemouth on 15 June 1874. The Bournemouth station eventually became Bournemouth West. Somerset & Dorset trains transferred from the Hamworthy station to the new Poole station immediately, and extended to Bournemouth as soon as the extension was opened. They still had to reverse at Wimborne, as the Corfe Mullen connection did not materialise until 1885.
The Bath extension
[edit]
In earlier times the port and industrial centre of Bristol had been the northerly magnet, but in the intervening years other railways had interposed themselves. But the Midland Railway's Mangotsfield and Bath Branch Line had reached Bath in 1869, so the S&DR decided to head for that destination. This had the advantage also of crossing the Somerset Coalfield.[19]
An act of Parliament[which?] was obtained on 21 August 1871 which included running powers for the last half mile into Bath over the Midland's line, and the use of their Bath station at Queen Square. The terrain was quite different from the previous ground covered, and engineers had to build many tunnels and viaducts. The line was steep, with a ruling gradient of 1 in 50. The summit, in the Mendip Hills, was 811 feet above sea level. (247 m).[19] From Radstock to Midford the railway followed the route of the Radstock branch of the Somerset Coal Canal which was little used and had been replaced by a tramway on the canal's towpath in 1815. The S&DR purchased the waterway, filled in the canal, removed the tramway and built its railway along the route. This greatly reduced the cost and time of construction and provided a mostly level course, but forced the railway to follow the sharply-curved course of the original canal.

Completion was swift, despite a break in construction when a contractor had financial problems. It opened on 20 July 1874.
There were four passenger trains each way every day; two of them carried through coaches from Birmingham to Bournemouth.
Intermediate stations were at Wellow, Radstock, Chilcompton, Binegar, Masbury, Shepton Mallet and Evercreech New. The original Evercreech station was renamed Evercreech Junction.
Financial exhaustion and lease
[edit]The completion of the line to Bath brought a further massive traffic increase, but the financial burden of the loans taken to build the Bath extension weighed the little company down even more, and it soon became clear that even day-to-day operating expenses could not be met. Atthill[12] describes the Bath extension project as an act of financial suicide.
| Somerset and Dorset Railway Leasing Act 1876 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Citation | 39 & 40 Vict. c. cxv |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 13 July 1876 |
The company realised that the game was up, and sought purchasers. The GWR and the B&ER were obvious candidates, but in August 1875 a 999-year lease was abruptly agreed jointly to the Midland Railway and the LSWR (the two railways whose networks it joined at either end), and this was confirmed by act of Parliament, the Somerset and Dorset Railway Leasing Act 1876 (39 & 40 Vict. c. cxv) on 13 July 1876.
The purchase price was generous, being calculated by the Midland and LSWR as much to exclude the GWR and B&ER from Bournemouth as anything else, and the rental income enabled the S&DR company to pay its shareholders 3+1⁄2%, a considerable income in those years of very low inflation.
The railway route was now the Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway.
The Joint Committee
[edit]With the lease to two very powerful companies, the operation of the Joint Line (as it was now called) would no longer be hampered by shortage of money. The Midland Railway and the LSWR set up a joint committee, and divided up responsibilities so that the Midland was in charge of motive power, and the LSWR provided the infrastructure and rolling stock.
The serious accident at Foxcote, near Radstock took place on 7 August 1876,[20][21] within a month of the formal takeover of responsibilities, and must have brought home to the parent companies the urgency of their intervening to bring things into good order. Operation of the complex stretches of single line had been done by Absolute Block working, but without any form of physical train staff (supplemented by telegraphic train orders issued from an office at Glastonbury), so the LSWR set about replacing this by the Electric Train Tablet method of single-line control.
Aside from that, the new management consolidated the links with mineral extraction interests near the line.
At Wells, two other railways, originally independent, had approached the S&D station there (Priory Road). The East Somerset line from Witham led in from the east, and had a station opposite the S&D station. The Bristol & Exeter operated branch from Yatton to a station in Wells at Tucker Street. The S&D station sat exactly between them and while these railways remained broad gauge, connecting them, a connection was difficult. Eventually they were absorbed by the GWR, and then converted to standard gauge, and on 1 January 1878 a through connection was made, so that goods traffic exchange was now possible, and GWR passenger trains could run throughout from Yatton to Witham, through the S&D station. They did not make calls there until 1 October 1934, and ceased to do so when the S&D Wells branch closed in 1951.

The main line transit from Bath to Bournemouth was still hampered by the necessity of reversing at Wimborne, and the joint companies built a new cut-off line from Bailey Gate, through the station in Corfe Mullen and the hamlet of Ashington, to what became Broadstone station. The new line ran alongside the Wimborne line for the first two miles to Corfe Mullen and the cut-off carried its first goods traffic on 14 December 1885, and was fully brought into use on 1 November 1886. It is not clear why the ten-month delay took place, but it may be connected with objections from the town of Wimborne at the obvious loss of train services.
In 1889 and 1891 the Midland Railway and the LSWR bought out nearly all of the stock of the original S&D shareholders, so that they finally became joint owners of the line.
Bridgwater joins the S&D
[edit]The original Somerset Central Railway company had considered the important town of Bridgwater as its western terminus, but had decided that the difficulties of constructing a route were too great. However the Bridgwater Railway Company made the connection from Edington Road, renamed Edington Junction, to Bridgwater, opening the seven mile line on 21 July 1890; there was one intermediate station at Cossington and a Halt at Bawdrip.[22] From that time, there was a viable passenger transit from Bridgwater to London via Templecombe, in competition with the GWR route via Bristol.
The nominally independent Bridgwater Railway had a working arrangement with the LSWR and the line was operated from the outset by the S&D. After the 1 January 1923 Grouping ownership of the line passed to the Southern Railway.[23]
Working of single line
[edit]From the late 1870s a number of the single line sections were made double track, to improve handling of the heavy train service, and by 1905 about two-thirds of the main line mileage was double track, and trains could now run throughout from Bath to Bournemouth with reasonable convenience, excepting only the awkward arrangement at Templecombe. Southbound trains calling there (to make connection into the LSWR Exeter main line) had to be hauled back to the S&D junction by a spare engine, then to continue their southward journey; the corresponding evolution in reverse was necessary for northbound trains. This complexity persisted until the final closure of the S&D line.
However the remaining single line sections proved a serious delaying factor for the traffic. Safety on single line sections was secured by every train carrying a token for each single line; instruments at the signal boxes were electrically interlocked to ensure that only one token could be out of the instruments for any one section at a time. The tokens had to be handed to the driver of every train by the signalman, and in the case of express trains, this meant slowing to walking pace to secure the handover.
Alfred Whitaker, the S&D locomotive engineer, developed a mechanical apparatus; part of this fitted to the locomotive cabside consisted of jaws which caught a loop on a pouch containing the token; the pouch was held at the lineside in a special delivery holder. The token to be given up by the train was correspondingly caught by a catcher fixed at the lineside.
This system enabled token exchanges to take place at 40 mph, and considerably accelerated the handling of through trains at single line crossing places.
The main line was single from Bath Junction to Midford (inclusive), from Templecombe Junction to Blandford with crossing places at Stalbridge, Sturminster Newton, Shillingstone and Stourpaine, and from Corfe Mullen to both Wimborne Junction and Broadstone Junction.
Locomotives and rolling stock
[edit]Locomotive and rolling stock on the Somerset and Dorset was largely defined by those running the line, the 5 main phases were:
- Somerset and Dorset, 1863–1875
- S&DJR – Midland Railway and LSWR, 1875 – 1923
- Post grouping – LMS and Southern Railway (SR), 1923–1948
- Nationalisation – British Rail Southern Region, 1948–1958
- Nationalisation – British Rail Western Region (north of Templecombe) and Southern region (south of Templecombe), 1958–1966
The early locomotive fleet was bought in from suppliers, and as the company was always in financial difficulties, the stock was never to the highest specification.
The company had its own Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon works at Highbridge.This closed in 1930 and the locomotives were transferred to the control of the LMS.
Things improved considerably when the Joint ownership started, and the Midland Railway provided more powerful and reliable traction. Even so, the Midland Railway's policy of building small engines was spectacularly unsuitable for the heavy gradients and heavy loads of the S&D.
For many years, right up to 1959, a Midland design of 4-4-0 Class 2P was the mainstay of the express passenger traffic, with variations of 3F 0-6-0 freight tender engine and 0-6-0T tank engines. A revolutionary change took place when the Midland built a small fleet of 2-8-0 tender engines to handle the heaviest freight trains—the unique S&DJR 7F 2-8-0 series—with Walschaerts valve gear and the greatest tractive effort ever delivered by a Derby locomotive, with the exception of the "Lickey Banker" 0-10-0.
After nationalisation in 1948 the Southern Region Battle of Britain and West Country 4-6-2 locomotives were a common sight. The heavier Merchant Navy 4-6-2 was not used on the line.



In the final few years, GWR Collett 0-6-0 tender locomotives in the 22XX class handled all of the Highbridge branch work, and LMS standard Jinty types dealt with the shunting duties. The LMS 4F 0-6-0 tender locomotives worked some trains down from Bath—they were commonplace on the Bath to Bristol services—and the Western Region drafted in green liveried Standard Class 5 4-6-0s in the 73XXX series, with BR Standard Class 4 4-6-0 75XXX 4-6-0 locomotives working from the Bournemouth end. The 7F 2-8-0s were pressed into passenger service in summer.
Some standard tanks classes operated on the line, the most powerful being the Standard Class 4 2-6-4T in the 80XXX series; these had one disadvantage, in that the water tanks extended along the cabside and this prevented the fitting of the Whitaker tablet exchange mechanism there.
In the early 1960s (1960 to 1963, to be exact) a small fleet of Standard Class 9F 2-10-0 locomotives were transferred to the line for the duration of the summer timetable period (roughly June to September) to work on the heaviest passenger trains. They included (in 1962) No. 92220 "Evening Star", the last steam engine to be built by British Railways. These locomotives proved ideal for the S&D, delivering considerable power, good steaming, and high adhesion. These heavy freight locomotives had relatively small wheels, and were not designed to run with passenger trains, but with the Pines Express they were easily able to reach, and perhaps exceed, the 70 mph line speed limit on the better, downhill parts of the route. After a review of the velocities of the reciprocating masses and coupling rods, a 60 mph maximum speed was urgently imposed.
Diesel multiple units were trialled on the route about 1959 when dieselisation of branch lines was in full swing elsewhere, but their relatively low power made them impractical for the steeply graded route.
Service in 1938
[edit]
The S&D's domestic train service was not fast, and except on summer Saturdays, there were a handful of stopping services, several of them running from Bath to Templecombe and from Templecombe to Bournemouth separately, and even the through stopping trains waited for some time at Templecombe. Some trains ran from Highbridge to Templecombe, and a few of the trains started from Bristol, reversing at Bath. (All these comments apply "and vice versa" wherever appropriate.)
The 1938 Bradshaw[24] gives a good snapshot of the train service:
Stopping trains took the best part of four hours for the Bath to Bournemouth journey. In July 1938 stopping trains left Bath Queen Square at
- 06:50 (Bristol Temple Meads] to Bournemouth)
- 08:30 (to Templecombe)
- 09:20 (Bristol Temple Meads to Bournemouth fast, 2 hours 35 minutes Bath to Bournemouth)
- 10:20 Clifton Down via Bristol Temple Meads to Bournemouth semi-fast, 2 hours 35 minutes Bath to Bournemouth)
- 13:10 (to Templecombe)
- 14:50 (to Templecombe; 15:00 on Saturdays)
- 17:05 (to Templecombe)
- 18:35 (to Bournemouth)
- 21:00 (to Evercreech Junction, continuing to Wincanton on Wednesdays and Templecombe on Saturdays)
- 23:00 to Midsomer Norton
The last train of the day from Bournemouth to Templecombe terminated there at the lower platform instead of reversing into the Upper station. A summer Sunday evening train started from the Lower Platform and ran to Bournemouth Central, but there were only one or two trains on Sundays.
The connections at Templecombe were poor, and this probably reflects timetable improvements over the years on the Waterloo – Salisbury – Exeter line that were not supported by S&D connectional arrangements. The early possibility of making a fast Bridgwater to Waterloo journey via Templecombe had vanished by 1938.
Summer Saturdays increased this traffic immensely over the domestic business; holidaymakers returning home wanted to leave Bournemouth in the morning, but the southbound arrivals travelled later in the day (having left northern towns in the morning).
There were thirteen long-distance trains handled over the S&D, all but one of them with Bournemouth as their southern terminal. The exception ran to Sidmouth and Exmouth, leaving the S&D at Templecombe; in later years it ran from Cleethorpes, forming an interesting coast-to-coast service. The holiday trains otherwise avoided Templecombe, and many ran non-stop from Bath to Poole taking two and a half hours from Bath to Bournemouth. The northern terminals were mainly on the former Midland Railway system, with Bradford in the lead, although the Pines Express ran to and from Manchester. Two southbound trains and one northbound train started on Friday night and ran through the small hours.
Branch lines
[edit]Six trains a day ran on the Highbridge line from Burnham-on-Sea to Evercreech Junction taking about 70 minutes for the 24 miles – two morning trains continued to Templecombe. A seventh train ran as the last of the day from Burnham-on-Sea to Wells, and the first train of the day in the reverse direction also ran from Wells to Burnham-on-Sea. In addition there were eleven daily trains in summer between Highbridge and Burnham-on-Sea only.
The Wells to Glastonbury line saw six trains each way daily, and the Bridgwater branch had eight trains each way (plus one Wednesdays only down train) daily. These more or less connected with trains for Evercreech at Edington Junction.
Closures
[edit]
The line began to decline in use from the 1950s onwards. In 1951, the branch from Glastonbury to Wells was closed. In December 1952, passenger services were withdrawn on the branch from Edington Junction to Bridgwater (Edington Junction being renamed 'Edington Burtle'); followed by closure of the branch on 1 October 1954.[23][25] The short section of branch-line from Highbridge to Burnham-on-Sea closed to regular services in 1951, though through specials continued to use the line until September 1962.[26] Highbridge was the new branch terminus and was renamed several times, becoming: Highbridge & Burnham-on-Sea.[26] In 1956 four of the smaller stations on the Dorset section of the main line were closed as an economy measure.
In 1958 management of the line north of Templecombe was transferred from the Southern Region of British Railways to the Western Region of British Railways. In the five years after this, through trains from the north and the Midlands were diverted to other routes, notably the daily Pines Express, which was re-routed after the end of the summer timetable in 1962.
In Summer 1962, John Betjeman (before his knighthood) visited the Somerset and Dorset to make a short BBC documentary, entitled "Branch Line Railway", first broadcast in March 1963. Starting at Evercreech Junction, Betjeman travelled the 24-mile stretch to Highbridge and Burnham-on-Sea, making a plea for this branch line to be spared by Dr. Beeching. The black-and-white film was issued on video by BBC Enterprises in 1987.[27]
A further small closure affecting the S&D in 1965 of the Bournemouth West terminus station saw S&D trains in the last months starting from and ending at Bournemouth Central.
Despite the Labour government elected in 1964 promising no further major railway cutbacks, an active campaign to save the line was lost when on 6 September 1965, the closure consent covering most of the S&D and the line to Bristol via Mangotsfield was issued.[28] Tom Fraser was the Minister of Transport at the time. That consent was followed by another for Broadstone station and Creekmoor Halt as these stops had also been served by another passenger service, though that had already been withdrawn.[29]
Closure scheduled for 3 January 1966 was deferred when one of the road operators withdrew his application for a licence to provide some of the alternative road services, and an emergency service was introduced on that date instead. This reduced the number of trains departing Bath to four a day (06:45, 08:15, 16:25 and 18:10), and two a day (06:55 and 16:00) from Highbridge. There were no through trains other than the 18:46 from Bournemouth Central on Saturdays, with journeys being broken at Templecombe and no suitable connections provided. There were no services on Sundays. Finally, on 7 March 1966 the whole S&D line from Bath to Bournemouth – and also the Evercreech Junction to Highbridge line – was closed under the Beeching Axe and dismantled. Three short sections survived:
- Blandford Station remained open for freight only, accessed by a branch from Broadstone until 1969.
- A section from the GWR main line at Highbridge to Bason Bridge remained opened to allow milk trains to access the United Dairies creamery. In the months before closure, goods trains loaded with fly ash tipped at the construction site of the M5 motorway to enable it to progress across the Somerset Levels. Progress on construction of the motorway finally closed the spur on 3 October 1972.[30]
- After the decision to close the S&DJR in 1966, a connection was made to the west of Radstock North with the GWR main line. This allowed trains on the former GWR Bristol and North Somerset Railway to traverse a short spur through Radstock North to Lower Writhlington Colliery, Braysdown Colliery and Writhlington Colliery, to transport coal to Portishead power station. After the last coal from the Somerset Coalfield was extracted from Writhlington Colliery on 28 September 1973, the spur was dismantled
Accidents
[edit]- Foxcote (Radstock) collision, 1876
- On 13 April 1914, a passenger train hauled by locomotive No. 52 was derailed at Burnham-on-Sea.[31]
- Bath goods yard 20 November 1929 3.25. An S & D locomotive 2-8-0 no 89 ran out of control from the Combe Down tunnel when the crew were overcome by fumes. The loco crashed into the goods yard at Green Park Station killing the driver and two others.[32]
- Braysdown Accident. On 29 July 1936, the crew of an empty colliery wagon train at Foxcote mistakenly abandoned their engine. The wagons were derailed, but no one injured.[33]
- On 19 August 1949, a British Railways passenger train from Highbridge collided with an Eclipse narrow gauge diesel locomotive crossing on the level and left the track, ending up in the Glastonbury Canal.[31][34] From 1922 onwards, the Eclipse Peat Works 2 ft (610 mm) industrial tramway had a level crossing on the SD&JR Burnham-on-Sea branch, .5 miles (0.80 km) west of Ashcott railway station.[35] The collision occurred when the tram locomotive stalled on the Eclipse level crossing on the SD&JR branch further towards Glastonbury.The locomotive was cut up into pieces and removed.
Restoration, renovation and preservation
[edit]Sections of the line are being restored. These include:
Somerset & Dorset Railway Heritage Trust
[edit]The Somerset & Dorset Railway Heritage Trust is based at Midsomer Norton South station. It operates a one-mile section of line on the original trackbed heading south from Midsomer Norton towards Chilcompton. Public trains ran every two weeks in 2019.[36]
The North Dorset Railway
[edit]The North Dorset Railway (formerly the Shillingstone Railway Project) is based at Shillingstone railway station. This heritage railway attraction intends to run standard gauge trains and aims to restore the line between the sites of Sturminster Newton and Stourpaine and Durweston as well.[37]
Gartell Light Railway
[edit]There is also a narrow gauge line south of Templecombe – the Gartell Light Railway – which uses a short section of S&D trackbed, with a planned extension northwards to Templecombe.[38][39]
Somerset and Dorset Railway Trust
[edit]The Trust was originally set up as the Somerset & Dorset Circle in late 1965 - before the line closed. In 1970, the Trust acquired S&D 7F locomotive No. 53808 from Woodham Brothers' Barry Scrapyard. The locomotive returned to steam in 1987. At Washford on the West Somerset Railway the Somerset and Dorset Railway Trust operated a museum of historical items and rolling stock originating from the S&D.[40] As of summer 2021, the stock and artefacts are being relocated owing to the Trust having been served with a Notice to Quit the site in February 2020.[41]
The New Somerset and Dorset Railway
[edit]A group called the New Somerset and Dorset Railway,[42] has been set up with the aim of restoring the line between Bournemouth and Bath, along with key branch lines, as a commercially viable railway running freight and commuter services (with provision for heritage services too). The group was formed 6 March 2009 as a reaction to climate change, peak oil, capacity restraints on the existing railway network and inefficiency in other forms of transport. Their intention is to buy up stretches of trackbed and buildings, as well as lobbying local and national government and encouraging restoration work along the line. They aim to present a document 'The Case for a New S&D' soon.[43] The first step is the purchase of the site of Midford station,[44] and restore it for use as an information office and operating base, although track will be re-laid (possibly towards Wellow) as part of the route reopening. The New S&D also started restoring Spetisbury station in Dorset in cooperation with Dorset County Council; this was to echo the role of Midford but with the addition of refreshment facilities.[45] However, the Spetisbury group is now independent, see below.
Non-railway use preservation
[edit]North Dorset Trailway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sources[46] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bath Green Park station has been fully preserved. With road access gained over the former railway bridges, in the former goods yard and approach roads Sainsbury's have developed a supermarket, while the main train shed houses a series of small businesses and a twice-weekly market.[47]
A short section of the former railway forms the North Dorset Trailway, a multi-use rail trail. The trail currently extends from Sturminster Newton to Spetisbury with plans to continue a further 5km northwest to Stalbridge.[48][49]
Two Tunnels Greenway
[edit]The section from Bath Green Park to Midford was bought and retained by Bath Council as part of their Two Tunnels Greenway. Under the management of Sustrans, who input £1M of the £1.9M project cost, the scheme provides a dual walking and cycle path from the centre of Bath to Midford, where it intersects with National Cycle Route 24. In July 2010, the council transferred the care of the Devonshire and Combe Down Tunnels to Sustrans. The section was opened on 6 April 2013.[50]
Spetisbury Station Project
[edit]This is a Community Interest Company (CIC) which has been clearing and improving the station site at Spetisbury, Dorset,with a long-term objective of creating a small railway heritage centre. Originally part of the 'New S&D' referred to above, the group subsequently became independent.
Glastonbury Festival
[edit]The trackbed from Steanbow Crossing to Cock Mill Crossing, between the sites of Pylle and West Pennard stations, crosses the site of the Glastonbury Festival and functions as an internal road within the festival site. There are gates at both points where it crosses the perimeter fence.
Maesbury Railway Cutting
[edit]Maesbury Railway Cutting between East Horrington and Gurney Slade is a Geological Conservation Review site because it exposes approximately 135 metres (443 ft) of strata representing the middle and upper Lower Limestone Shales and the basal Black Rock Limestone. Both formations are of early Carboniferous (Courceyan) age.[51]
Preserved S&DJR locomotives
[edit]| Image | S&DJR No. | S&DJR Class | Type | Manufacturer | Serial No. | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
88 | 7F | 2-8-0 | Robert Stephenson and Company | 3894 | July 1925 |
At the Mid Hants Railway |
 |
89 | 7F | 2-8-0 | Robert Stephenson and Company | 8395 | July 1925 |
At the North Norfolk Railway |
Neither of the S&DJR Sentinels has been preserved but a similar locomotive is operational at Midsomer Norton railway station.[52]
Preserved rolling stock
[edit]
Four ex-S&DJR carriages have survived:
- No. 4 six-wheel first, built in 1886,[53] is preserved at Washford on the West Somerset Railway and is currently operational in S&DJR livery and owned by Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust. It was grounded at Templecombe and was preserved from the site in 1986.[54]
- Two other six-wheel carriages are preserved by the Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust on the West Somerset Railway;
- Section of a four-wheel passenger brake has also been preserved by the Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust.[57]
- No. 2 four-wheel first, was grounded at West Huntspill but was broken up by the Somerset and Dorset Railway Trust for spares around March 1994.[58]
- No . 9 Brake Van, was in a field at Highbridge and was recovered by the SDRT around October 2001, it was faintly marked 'Wells Branch', 'S D J R' and 'No 9'.[59]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e The Railway Year Book for 1926. London: The Railway Publishing Company Limited. 1926. pp. 197–198.
- ^ a b Peters, Ivo (1974). The Somerset and Dorset — An English Cross Country Railway. Oxford Publishing Company. p. 1. ISBN 0-902888-33-1.
- ^ Awdry, Christopher (1990). Encyclopaedia of British Railway Companies. Patrick Stephens Ltd. Page 237.
- ^ a b Casserley, H.C. (1968). Britain's Joint Lines. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0024-7.
- ^ "North Somerset Heritage Trust". Archived from the original on 26 May 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ Green-Hughes, Evan (2012). Lightweight DMUs. The early Derby Works and Merto-Cammell units. Hersham, Surrey: Ian Allan. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-7110-3463-1.
- ^ "East Dorset Railways". Martin Rowley. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ Horsfall, Bill (2014). London Midland & Scottish. Author House. pp. 17–18. ISBN 9781496981783. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Atterbury, Paul (2011). Paul Atterbury's Lost Railway Journeys. David & Charles. pp. 28–30. ISBN 9781446300954.
- ^ "Somerset & Dorset last summer Saturdays". Heritage Railway. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ a b c Beale, Mike (January 2008). "150 Years of the Somerset & Dorset Railway" (PDF). Back Track: 25–30. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 September 2015. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- ^ a b c d Robin Atthill & O. S. Nock, 1967. The Somerset & Dorset Railway. Newton Abbot: David & Charles. ISBN 0-7153-4312-2.
- ^ "Somerset Central Railway (S&DJR)". John Speller. Archived from the original on 12 September 2016. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- ^ "Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway". Southern E-Group. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ Historic England. "Burnham-on-Sea Pier (617573)". Research records (formerly PastScape). Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway, Stephen Austin, Ian Allan Publishing, 1999.
- ^ "Templecombe Junction Railway". Train Web. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ Atthill, Robin (1964). Old Mendip. Newton Abbott: David and Charles. ISBN 0-7153-5171-0.
- ^ a b Yorke, Stan (2007). Lost railways of Somerset. Newbury: Countryside Books. pp. 48–60. ISBN 978-1-84674-057-2.
- ^ Norbury, s. G. (10 August 2015). "Looking back: Fifteen dead in Radstock rail crash". Somerset Guardian. Archived from the original on 19 December 2015. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- ^ "Train tragedy of 1876 recorded by local poet". Western Daily Press. 29 July 2010. Retrieved 29 December 2015.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Thomas, David St John, (1966). A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain, Volume 1: The West Country, (Third edition), Newton Abbot: David & Charles
- ^ a b Awdry, Christopher (1990). Encyclopaedia of British Railway Companies. Partick Stephens Ltd. Page 179.
- ^ Bradshaws July 1938 Railway Guide (reprint ed.). Newton Abbot: David & Charles. 1969. ISBN 0-7153-5824-3.
- ^ Harrison, J.D. (1981). The Bridgwater Railway. Locomotion Papers, LP132. Headington: The Oakwood Press. ISBN 0-85361-403-2.
- ^ a b Butt, R.V.J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations. Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-85260-508-1.
- ^ Geegs (28 December 2017). "Lets Imagine – A Branch Line Railway with John Betjeman". YouTube. Archived from the original on 9 March 2019. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ Letter from the Ministry of Transport to the Secretary of the British Railways Board, 6 September 1965. Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust archive ref. WSHSD_2019_5_6.
- ^ Letter from the Ministry of Transport to the Secretary of the British Railways Board, 17 September 1965. Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust archive ref. WSHSD_2019_5_7.
- ^ "Historical East Huntspill in Somerset". East Huntspill Parish Council. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ^ a b Trevena, Arthur (1980). Trains in Trouble. Vol. 1. Redruth: Atlantic Books. pp. 26, 44. ISBN 0-906899-01-X.
- ^ "The Somerset & Dorset Railway - Accidents". Archived from the original on 7 February 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2012.
- ^ E. Woodhouse (8 December 1936). "Correspondence | licensed by The Railways Archive under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 2.0" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- ^ "Accidents". SDJR.net. Archived from the original on 7 February 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2012.
- ^ "Ashcott". SDJR.net. Archived from the original on 7 February 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2012.
- ^ "Home". The Somerset & Dorset Railway Heritage Trust. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ "Shillingstone Railway Project". Shillingstone Railway Project. Archived from the original on 14 March 2015. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ "Gartell Light Railway". Gartell Light Railway. Archived from the original on 4 February 2013. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ "The Somerset & Dorset Evercreech Junction to Bournemouth West and Bournemouth Central". Cornwall Railway Society. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ "The Trust Museum". Somerset & Dorset Railway Trust. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ "Trust receives 12 months notice to quit Washford site • S&DRT". S&DRT. 20 February 2020. Retrieved 9 September 2021.
- ^ "The New Somerset and Dorset Railway – Official website". Somersetanddorsetrailway.co.uk. Archived from the original on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ^ "New dawn fades". Somerset and Dorset Blogsite. 2 November 2007. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2007.
- ^ "Appeal to buy Midford station launched". Heritage Railway (125). Morton Media Group: 9. 11 June 2009.
- ^ "About Us". New Somerset & Dorset Railway. Archived from the original on 2 March 2013. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ "Welcome to North Dorset Trailway Network". www.northdorsettrailway.org.uk. Archived from the original on 8 June 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ "Green Park Station, Bath". Ethical Property. Archived from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ "The North Dorset Trailway Network". The North Dorset Trailway Network. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 6 June 2014.
- ^ "North Dorset Trailway extension connects Blandford and Stourpaine". BBC News. 15 May 2013. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
- ^ "Two Tunnels Shared Path". Archived from the original on 26 January 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ "Maesbury Railway Cutting" (PDF). SSSI citation sheet. English Nature. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 March 2009. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ^ Andy Chapman (17 October 1964). "Sentinel Steam Loco 7109: What is Sentinel 7109?". Sentinel7109.blogspot.com. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ^ "Somerset Dorset Joint 4 Six-wheel First body: on chassis ex LMS CCTZ 6589 built 1886". Railway Heritage Register. Archived from the original on 26 December 2015.
- ^ "86-04-018". Flickr. 18 July 1986. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ "Somerset Dorset Joint 114 S&DJR; Six w 3rd (body only; on LMS Six-w u'frame) built 1890". Railway Heritage Register. Archived from the original on 27 December 2015.
- ^ "Somerset Dorset Joint 98 S&DJR; 6 w 3rd (body only; temp on LMS 6-w u'frame) built 1894". Railway Heritage Register. Archived from the original on 26 December 2015.
- ^ "Somerset Dorset Joint 4 Wheel Passenger Brake section (body only)". Railway Heritage Register. Archived from the original on 26 December 2015.
- ^ "94-01-016". Flickr. 6 March 1994. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ "S&DJR Wells Brake Van No. 9". Flickr. 27 February 2000. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- Cobb, Col M.H. (2003). The Railways of Great Britain: A Historical Atlas. Ian Allan Publishing Ltd. ISBN 0-7110-3002-2.
Further reading
[edit]- Adley, Robert (1988). Covering My Tracks. Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 0-85059-882-6.
- Atthill, Robin (1967). The Somerset and Dorset Railway. David and Charles. ISBN 0-7153-4164-2.
- Daniels, Gerald David; Dench, Leslie Alan (May 1973) [1964]. Passengers No More (2nd ed.). Shepperton: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0438-2. OCLC 2554248. 1513 CEC 573.
- Harper, Duncan (1998). The Somerset & Dorset Railway: Opening of the Bath Extension 1874. Bath: Millstream Books. p. 47. ISBN 0-948975-49-0.
- Hawkins, Mac (1986). The Somerset & Dorset Then and Now. London: Guild Publishing.
- Lucking, J.H. (1968). Railways of Dorset. Railway Correspondence and Travel Society.
- Mitchell, Vic; Smith, Keith (January 1992). Branch Lines Around Wimborne. Middleton Press. ISBN 0-906520-97-5.
- Mitchell, Vic; Smith, Keith (November 1998). Country Railway Routes: Bath to Evercreech Junction. Middleton Press. ISBN 0-906520-60-6.
- Oakley, Mike (2002). Somerset Railway Stations. Midhurst: Dovecote Press.
External links
[edit]- "Archival material relating to Somerset & Dorset Joint Line Railway". UK National Archives.
- "Archival material relating to Somerset & Dorset Railway Co". UK National Archives.
- Google map showing route of Somerset & Dorset Railway
- North Dorset Railway (formerly Shillingstone Station Project)
- Platform 14 Ltd (27 April 2008). "Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway". Along These Lines. Season 1. Episode 3. ITV Meridian. Archived from the original on 24 July 2008.
- Somerset and Dorset Railway Heritage Trust at Midsomer Norton
- Somerset and Dorset Railway Trust
- S&DJR Photographic Route Map
- S&DJR Signalling
- S&DRT History
- Accidents at The Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway