Interval signal
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (January 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|

An interval signal, or tuning signal, is a characteristic sound or musical phrase used in international broadcasting, numbers stations, and by some domestic broadcasters, played before commencement or during breaks in transmission, but most commonly between programs in different languages.
It serves several purposes:
- It helps a listener using a radio with an analog tuner to find the correct frequency.
- It informs other stations that the frequency is in use.
- It serves as a station identifier even if the language used in the subsequent broadcast is not one the listener understands.
The practice began in Europe in the 1920s and 1930s and was carried over into shortwave broadcasts. The use of interval signals has declined with the advent of digital tuning systems, but has not vanished. Interval signals were not required on commercial channels in the United States, where jingles were used as identification.
List of interval signals by station
[edit] Radiodifusión Argentina al Exterior: First eight notes of "Mi Buenos Aires querido" by Carlos Gardel, followed by people saying the station's name in eight languages.
Radiodifusión Argentina al Exterior: First eight notes of "Mi Buenos Aires querido" by Carlos Gardel, followed by people saying the station's name in eight languages.
 Bangladesh Betar: A tune composed by Samar Das.
Bangladesh Betar: A tune composed by Samar Das.
 Radio Belarus: "Motherland, my dear" (Belarusian: Радзіма, мая дарагая, Russian: Родина моя дорогая) by Vladimir Olovnikov and Ales Bachyla.
Radio Belarus: "Motherland, my dear" (Belarusian: Радзіма, мая дарагая, Russian: Родина моя дорогая) by Vladimir Olovnikov and Ales Bachyla.
 Rádio Brasil Internacional: Xylophone version of "Brazilian Flag Anthem" (Brazilian Portuguese: Hino à Bandeira Nacional) by Antônio Francisco Braga and Olavo Bilac.
Rádio Brasil Internacional: Xylophone version of "Brazilian Flag Anthem" (Brazilian Portuguese: Hino à Bandeira Nacional) by Antônio Francisco Braga and Olavo Bilac.
 China:
China:
- China National Radio and China Radio International: Chime version of March of the Volunteers (义勇军进行曲).

- Voice of the Strait News Radio: Bell version of "Three Rules of Discipline and Eight Points for Attention" (三大纪律八项注意).

 Radio Habana Cuba: Melody of "March of the 26th of July" (La Marcha del 26 de Julio) by Agustín Díaz Cartaya.
Radio Habana Cuba: Melody of "March of the 26th of July" (La Marcha del 26 de Julio) by Agustín Díaz Cartaya. DR P1: "Drømte mig en drøm i nat", played on xylophone.[1]
DR P1: "Drømte mig en drøm i nat", played on xylophone.[1]

 Radio France Internationale: Electronic-disco, culminating in the last 8 measures of "La Marseillaise".
Radio France Internationale: Electronic-disco, culminating in the last 8 measures of "La Marseillaise". Deutsche Welle: Celesta version of "Es sucht der Bruder seine Brüder" from Fidelio by Ludwig van Beethoven.
Deutsche Welle: Celesta version of "Es sucht der Bruder seine Brüder" from Fidelio by Ludwig van Beethoven.
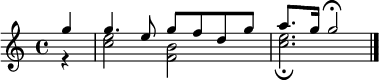
 Voice of Greece: "The Little Shepherd" (Ο Τσομπανάκος), played on floghera.[2]
Voice of Greece: "The Little Shepherd" (Ο Τσομπανάκος), played on floghera.[2] All India Radio: A tune composed by Walter Kaufmann or Thakur Balwant Singh, used since 1936.[3]
All India Radio: A tune composed by Walter Kaufmann or Thakur Balwant Singh, used since 1936.[3]
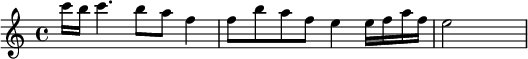
 Indonesia
Indonesia
- RRI Programa 3: Ending bars of "Solace on Coconut Island" (Rayuan Pulau Kelapa), composed by Ismail Marzuki.
- RRI Voice of Indonesia: "Feeling of Love" (Rasa Sayang).
 RTÉ Radio 1: Chime version of "O'Donnell Forever" (O'Donnell Abú).[4]
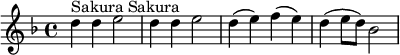
RTÉ Radio 1: Chime version of "O'Donnell Forever" (O'Donnell Abú).[4] Radio Japan:
Radio Japan:
- "Kazoe-uta" (数え歌, counting-out game).
- "Sakura Sakura" (さくらさくら, cherry blossoms).

 Radio Nepal: A tune composed by Ustad Govinda Lal Nepali.
Radio Nepal: A tune composed by Ustad Govinda Lal Nepali. North Korea
North Korea
- Voice of Korea: Melody of "Song of General Kim Il-sung" (김일성장군의 노래).
- Pyongyang FM: Melody of "Song of General Kim Jong-il" (김정일장군의 노래).
 KBS World Radio: "Dawn".
KBS World Radio: "Dawn". RTL Radio: "De Feierwon" by Michel Lentz, played on chimes.[5]
RTL Radio: "De Feierwon" by Michel Lentz, played on chimes.[5] Voice of Mongolia: "Motherland" (Эх орон).[citation needed]
Voice of Mongolia: "Motherland" (Эх орон).[citation needed]

 Radio New Zealand International: The call of a New Zealand bellbird
Radio New Zealand International: The call of a New Zealand bellbird Radio Pakistan: A tune composed by Khwaja Khursheed Anwar.
Radio Pakistan: A tune composed by Khwaja Khursheed Anwar.

 Philippines:
Philippines:
- Far East Broadcasting Company: "We Have Heard the Joyful Sound".
- Radio Veritas Asia: "O via, vita, veritas".
 Radio Romania International: The first nine notes of “Pui de lei", lyrics by Ioan S. Nenițescu and song by Ionel G. Brătianu
Radio Romania International: The first nine notes of “Pui de lei", lyrics by Ioan S. Nenițescu and song by Ionel G. Brătianu Russia
Russia
- Radio Mayak: Vibraphone version of Moscow Nights.
- Radio Sakha: Excerpt from a Yakut folk song.
 Radio Slovenia: Electronically generated cuckoo chirping.
Radio Slovenia: Electronically generated cuckoo chirping. Radio Ukraine International: "Roar and groan, vast Dnieper" (Реве та стогне Дніпр широкий).
Radio Ukraine International: "Roar and groan, vast Dnieper" (Реве та стогне Дніпр широкий). BBC World Service:
BBC World Service:
- English programme: "Bow Bells".
- Non-English programme, non-Europe: "Lillibullero", three notes tuned B–B–C.
- Non-English programme, to Europe: four notes tuned B–B–B–E.

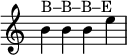
 United States:
United States:

- Trans World Radio: "What a Friend We Have in Jesus".
- Voice of America: Brass band version of "Yankee Doodle".
- WEWN, later EWTN Global Radio: "Salve Regina"
 Vatican Radio: "Christus Vincit", played on celesta.
Vatican Radio: "Christus Vincit", played on celesta.

 Radio Nacional de Venezuela's Canal Internacional: Beginning of "Alma Llanera" by Pedro Elías Gutiérrez and Rafael Bolívar Coronado.
Radio Nacional de Venezuela's Canal Internacional: Beginning of "Alma Llanera" by Pedro Elías Gutiérrez and Rafael Bolívar Coronado.
Formerly used
[edit] Radio Tirana: Këputa një gjethe dafine (transmission intro) and the trumpet version of With Pickaxe and Rifle.
Radio Tirana: Këputa një gjethe dafine (transmission intro) and the trumpet version of With Pickaxe and Rifle.

 Radio Australia: Chimes version of Waltzing Matilda (chorus), Kookaburra call. News signature tune: Majestic Fanfare.
Radio Australia: Chimes version of Waltzing Matilda (chorus), Kookaburra call. News signature tune: Majestic Fanfare. Radio Österreich International: Orchestral version of An der schönen blauen Donau ("Blue Danube Waltz") by Johann Strauss.[6]
Radio Österreich International: Orchestral version of An der schönen blauen Donau ("Blue Danube Waltz") by Johann Strauss.[6]

 Ö1: Three notes signifying O–R–F by Werner Pirchner, played on viola.[7]
Ö1: Three notes signifying O–R–F by Werner Pirchner, played on viola.[7]

 RTBF International: Où peut-on être mieux qu’au sein de sa famille.
RTBF International: Où peut-on être mieux qu’au sein de sa famille. Rádio Nacional: Luar do Sertão ("Hinterlands Moonlight").
Rádio Nacional: Luar do Sertão ("Hinterlands Moonlight"). Radio Canada International: First four notes of O Canada, played on piano or autoharp.
Radio Canada International: First four notes of O Canada, played on piano or autoharp.

 Radio Peking (predecessor of China Radio International): Chimes version of 东方红 ("The East Is Red").
Radio Peking (predecessor of China Radio International): Chimes version of 东方红 ("The East Is Red").
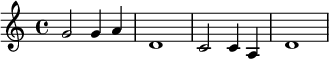
 Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation: Avkoritsa by Andreas Mappouras, played on guitar
Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation: Avkoritsa by Andreas Mappouras, played on guitar Radio Prague
Radio Prague
- Trumpet version of Kupředu levá ("Forward, Left") by Jan Seidl

 Yle Radio 1: Pim-pam-pulla by A. O. Väisänen.[8]
Yle Radio 1: Pim-pam-pulla by A. O. Väisänen.[8]

 Radio France Internationale: Trumpet version of a popular song, Nous n'irons plus au bois.[6]
Radio France Internationale: Trumpet version of a popular song, Nous n'irons plus au bois.[6]

 Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk: The 4th symphony by Brahms.
Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk: The 4th symphony by Brahms.

 Reichssender Berlin: Ending bars of Volk ans Gewehr, played on glockenspiel.
Reichssender Berlin: Ending bars of Volk ans Gewehr, played on glockenspiel.

 East Germany
East Germany
- Berliner Rundfunk: Motif from the opera Regina by Albert Lortzing, played by trumpets.
- Radio Berlin International: Beginning of Auferstanden aus Ruinen ("Risen from Ruins"), played on chimes.

-
Interval signal for Radio NTS
-
Interval signal for DFS 904
 Deutschlandfunk: Celesta version of Dir, Land voll Lieb' und Leben from "Ich hab' mich ergeben" by Hans Ferdinand Maßmann.[9]
Deutschlandfunk: Celesta version of Dir, Land voll Lieb' und Leben from "Ich hab' mich ergeben" by Hans Ferdinand Maßmann.[9]

 Radio Budapest: Excerpts from the suite 1848 by T.K. Polgar played on three trumpets and two cornets.
Radio Budapest: Excerpts from the suite 1848 by T.K. Polgar played on three trumpets and two cornets.

 Kol Yisrael: Trumpet and drum version of Hatikvah.
Kol Yisrael: Trumpet and drum version of Hatikvah.

 Rai Italia Radio: Mechanically generated canary chirping.
Rai Italia Radio: Mechanically generated canary chirping. Trans World Radio: Hymne Monégasque
Trans World Radio: Hymne Monégasque
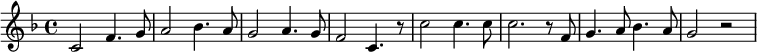
 Netherlands
Netherlands
- NPO: First seven notes of Wilhelmus, played on clarinet (Radio 1 and Radio 5), synthesizer (Radio 3), spinet (Radio 4) and flute (Radio 2).[10][better source needed]
- Radio Netherlands: Carillon version of the Eighty Years' War song Merck toch hoe sterck.

 Norway
Norway
- NRK P1: Motif from Sigurd Jorsalfar by Edvard Grieg.[11]
- Radio Norway International (Utenlandssendingen (in Norwegian), former international service of NRK): Symphony No. 1, Op. 26: Innover viddene. 1938, 51 by Eivind Groven

 Poland
Poland
- Radio Katowice: Sound of a hammer striking an anvil.[12]
- Radio Olsztyn: Excerpt from O Warmio moja miła by Feliks Nowowiejski, played on barrel organ.
- Polish Radio External Service: Excerpt from Prząśniczka by Stanisław Moniuszko, played on piano.[13]
- Radio Polonia: Piano version of Etude No. 12 ("Revolutionary Etude") by Frédéric Chopin.
![<<{\key c \minor \skip2 \skip8. <c'' c'''>16[ <d'' d'''>8. <es'' es'''>16] <es'' es'''>2 r8. <g'' es'' c'' g'>16[ <g'' es'' c'' g'>8.\< <g'' es'' c'' g'>16]\! <as'' es'' c'' as'>2\> <g'' es'' c'' g'>2\!} {\key c \minor \clef bass \skip2. es16\> d c g,\! c,\< g, c d es g c' d'\! es'\> d' c' g es d c g,\! c,\< g, c d\! es\> d c g,\! c,2}>>](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/3/r/3rm2511e9r59cn0f4muu17o40rkunvp/3rm2511e.png)
 Radio Bucharest 1 and Radio Bucharest External Service (pre 1989): Fragment from Cantata anilor luminǎ by Anatol Vieru
Radio Bucharest 1 and Radio Bucharest External Service (pre 1989): Fragment from Cantata anilor luminǎ by Anatol Vieru Voice of Russia: "Majestic" chorus from the "Great Gate of Kiev" portion of Pictures at an Exhibition by Mussorgsky.
Voice of Russia: "Majestic" chorus from the "Great Gate of Kiev" portion of Pictures at an Exhibition by Mussorgsky. Radio Serbia: Bože pravde.
Radio Serbia: Bože pravde. Radio Slovakia International: Kto za pravdu horí.
Radio Slovakia International: Kto za pravdu horí. Radio RSA (former international service of Apartheid-era South African Broadcasting Corporation): Bokmakierie chirping and first bars of Ver in die Wereld, Kittie, played on guitar.[6][14]
Radio RSA (former international service of Apartheid-era South African Broadcasting Corporation): Bokmakierie chirping and first bars of Ver in die Wereld, Kittie, played on guitar.[6][14]

 Radio Sweden: Chime version of Ut i vida världen ("Out in the Wide World"), composed by Ralph Lundsten and the opening notes of Carl Michael Bellman's Storm och böljor tystna r'en.[6][15]
Radio Sweden: Chime version of Ut i vida världen ("Out in the Wide World"), composed by Ralph Lundsten and the opening notes of Carl Michael Bellman's Storm och böljor tystna r'en.[6][15] Switzerland
Switzerland
- Radio Beromünster: D' Zit isch do, played on music box.
- Swiss Radio International: Lueget, vo Berg und Tal.

 Voice of Turkey: Turkish makam, played on piano.
Voice of Turkey: Turkish makam, played on piano.
Interval signal of Voice of Turkey as heard in 2013
 Radio Moscow (former international service of the Soviet Union):
Radio Moscow (former international service of the Soviet Union):
- Подмосковные вечера ("Moscow Nights"), played on vibraphone.
- Песня о Родине ("Wide Is My Motherland")

 BBC World Service: Trumpet version of Oranges and Lemons, first four notes of Symphony No. 5 by Beethoven, played on timpani; Lillibullero (signature tune, played on trumpet).[16]
BBC World Service: Trumpet version of Oranges and Lemons, first four notes of Symphony No. 5 by Beethoven, played on timpani; Lillibullero (signature tune, played on trumpet).[16] WYFR: First two bars of To God Be the Glory by William Howard Doane played by a brass band
WYFR: First two bars of To God Be the Glory by William Howard Doane played by a brass band Radio Yugoslavia (1980–1989): First bar of Druže Tito, ljubićice bjela anonymous Partisan song, in various orchestral renditions.[17]
Radio Yugoslavia (1980–1989): First bar of Druže Tito, ljubićice bjela anonymous Partisan song, in various orchestral renditions.[17]

 Radio Yugoslavia, later International Radio of Serbia and Montenegro: Jugoslavijo by Nikola Hercigonja.
Radio Yugoslavia, later International Radio of Serbia and Montenegro: Jugoslavijo by Nikola Hercigonja.
Classical radio station WQXR-FM in New York City, during its ownership by The New York Times Company, played different variations of a classical infused gong with the ID read at the same time as "The Classical Station of the New York Times, WQXR, New York (And WQXR.com 2000–2009) [citation needed]
Numbers station interval signals
[edit]Numbers stations are often named after their interval signals, such as The Lincolnshire Poacher or Magnetic Fields after "Magnetic Fields Part 1" by Jean-Michel Jarre.
References
[edit]- ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: stephensen (2009-10-19). "Pausesignal". Retrieved 2020-04-02 – via YouTube.
- ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: Ο τσομπανάκος σήμα ΕΡΤ). YouTube.
- ^ Tuning into broadcast history. The Hindu BusinessLine, 15 October 2015.
- ^ "'O'Donnell Abú'". RTÉ.ie.
- ^ "Pausenzeichen und ihre musikalischen Quellen". 8 October 2007.
- ^ a b c d Frost, Jens Mathiesen (1983). World Radio TV Handbook. New York: Billboard Publications.
- ^ Treiber, Alfred (2007). Ö1 gehört gehört : die kommentierte Erfolgsgeschichte eines Radiosenders (in German). Vienna: Böhlau. p. 218. ISBN 978-3-205-77495-2. OCLC 127107294.
- ^ "Radion väliaikamerkki". yle.fi. 4 July 2008.
- ^ "kalter-krieg-im-radio.de". www.kalter-krieg-im-radio.de.
- ^ nl:Pauzeteken
- ^ http://www.ontheshortwaves.com/Articles/The_Interval_Signal.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "- YouTube". www.youtube.com.
- ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: RADIO INTERVAL SIGNALS - "Radio Polonia". YouTube.
- ^ "DX Listening Digest 7-043".
- ^ Radio Sweden interval signal Retrieved 2011-11-24.
- ^ BBC World Service (Europe) interval signal Retrieved 2013-10-09.
- ^ "Top deset pjesama o Titu". vijesti.ba.
Further reading
[edit]- Sennitt, Andrew G. (1997). World Radio and Television Handbook 1997. Billboard Books. p. 560. ISBN 0-8230-7797-7.
- Sennitt, Andrew G.; David Bobbitt (December 2005). World Radio and Television Handbook 2006. Billboard Books. p. 608. ISBN 0-8230-7798-5.
External links
[edit]- Interval Signals Online
- Nobuyuki Kawamura's Interval Signal Library
- IntervalSignal DataBase (German) English version
- Uwe Volk's Sound Library (available both in English and in German)
- Kurzwelle-Historisch
- Interval signals on Live-Radio.net
